US $100.00
| Condition | Used
:
An item that has been used previously. The item may have some signs of cosmetic wear, but is fully operational and functions as intended. This item may be a floor model or store return that has been used. See the seller’s listing for full details and description of any imperfections.
|
| Seller Notes | “These items are for incorporation into the Agilent 81960A” |
Directions
Similar products from Laser Equipment

Fiber Optic Ring Light gooseneck fits 2.25 inch microscopes, 36 inch long

Fostec flexible double gooseneck Fiber optic 40 inches for illuminator

Laser Optic Lens CE #0560 Rotating Turret Mount 6 Positions, 4 Lenses

Alcon Labs 6309-0005 Laser Optic Lens & Mount 1.5" 0x-0.197"

Alcon Labs 6309-0005 Optic Lens w/Mount 1.5" 0x.197"

21mW + High Power Helium Neon Laser for Holography!

50R/50T Plate Beamsplitter 32x32x1.1mm. 1 Lot of 5x.

++ LASERMETRICS LASER ACCESSORY / DETECTOR P/N 311 PD

HAMAMATSU R928-14 PHOTO MULTIPLIER TUBE with board
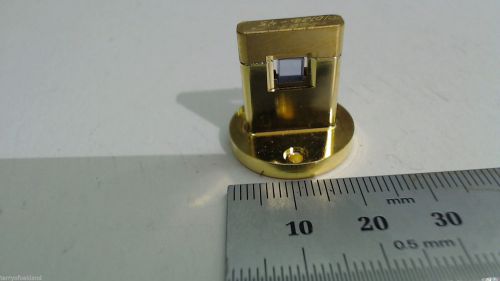
NdYVO4 Spectra Physics Laser Crystal

Newport Spectra Physics Bifurcated Fiber Optic Cable

Lucent M-E2580H FIber optic laser moduls 10mw 1550nm

Triquint D2525G46 Fiber Optic Laser Module 10mw 1550nm

Triquint D2526G33 Fiber Optic laser module 1550nm

Triquint D2526S25 Fiber Optics Laser module
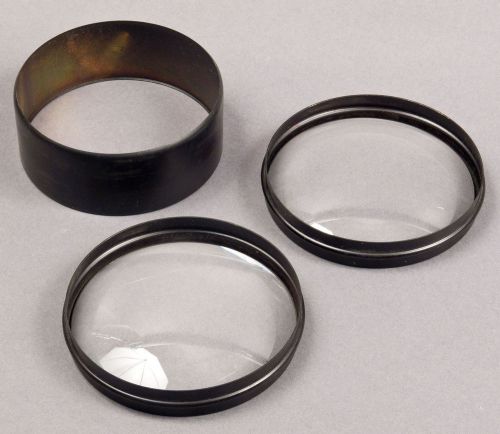

Large Brass Cased 4.45 inch Wide, Two Element Plano-Convex Condenser Lens Set

Made in USA for CO2 Gold plated Si mirror 20mm 40w laser engraver Fast shipping

OPTICAL CYLINDRICAL LENS LASER OPTICS BIN#A7-D-96
People who viewed this item also vieved

Gould TA6000 Micropulsing Thermal Array Chart Recorder free shipping

++ Carl Zeiss M4-QIII Lab Spectrophotometer
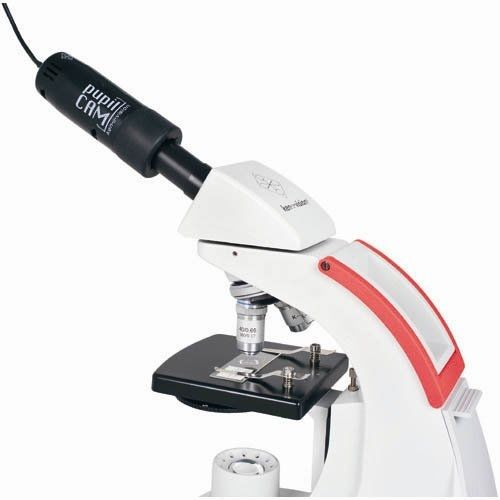
Ken-A-Vision 1401KRM PupilCAM Digital HD Microscope Camera with Rubber Adapter
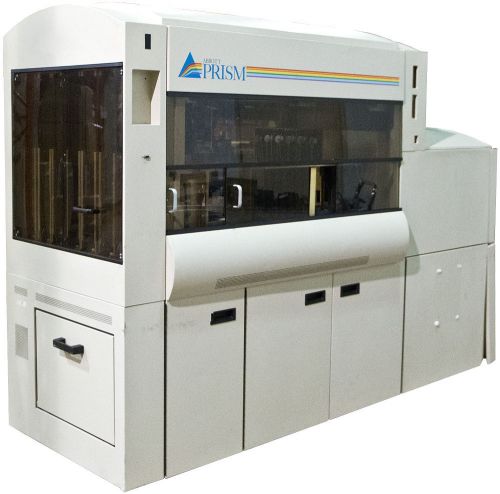

Abbott Prism In Vitro Chemiluminescent Immunoassay Analyzer w/Software installed
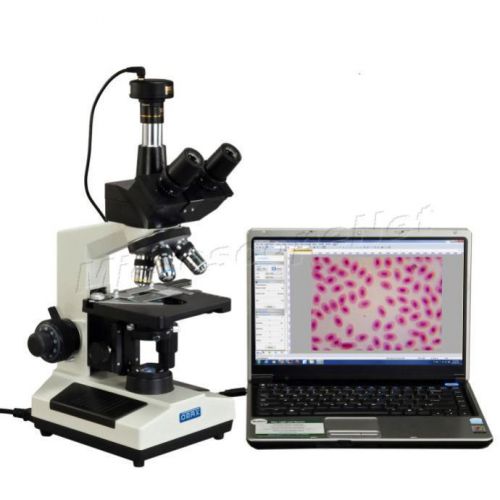
Lab Clinic Vet Trinocular Phase Contrast Compound Microscope+9MP Digital Camera

New Focus Newport 8752 8753 Ethernet Picomotor Controller System 8303 Actuators

Steris Amsco Sonic Bath Large Ultrasonic Cleaner Parts Washer with Warranty
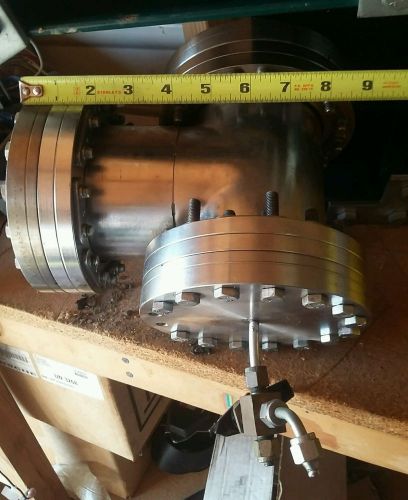

Huntington high vacuum chamber 7 5/8 x 9" Tee with 6" flange blanks Nupro valve

Boekel 131601 0731403 Digital Incubator Laboratory Scientific Oven 90W 120V .76A

FISHER Dyna-Mix - Model #143 - Controller

Yamato LR41B Labo-Stirrer Mixer
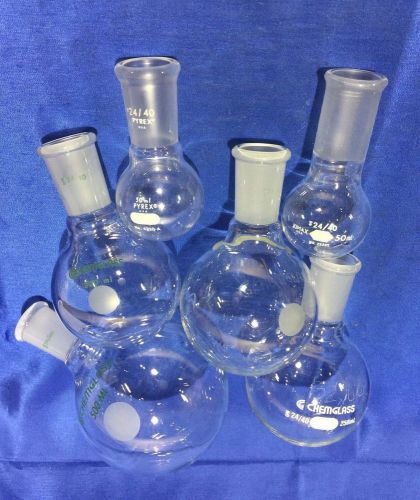

6 ea 24/40 Round Bottom Flask 500mL - 50mL

ZHENGZHOU GREAT WALL SCIENTIFIC ROTARY EVAPORATOR R1001- AAR 3381

Tuttnauer Brinkmann 2540E Sterilizer/Autoclave 10" Dia x 18" D S

Instek-GW GPC-3030 Power Supply,30V/3A Power Supplies

BARSNTEAD INTERNATIONAL Max-Q 2508 Shaker
By clicking "Accept All Cookies", you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Accept All Cookies